Expectations about future learning influence moment-to-moment feelings of suspense
Abstract
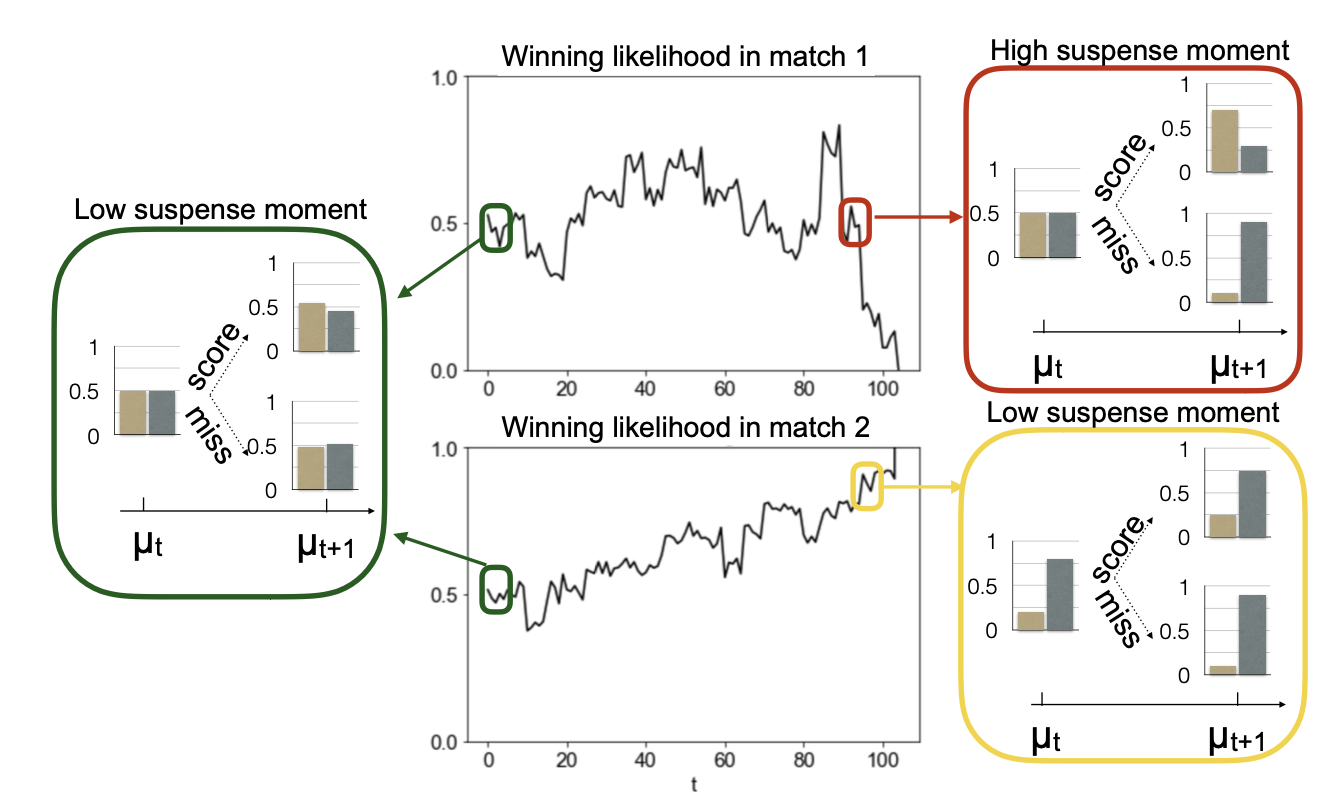
Suspense is a cognitive and affective state that is often experienced in theanticipation of information and contributes to the enjoyment and consump-tion of entertainment such as movies or sports. Ely, Frankel, and Kamenica(2015) proposed a formal definition of suspense which relies upon predictionsabout future belief updates. In order to empirically evaluate this theory, wedesigned a task based on the casino card game Blackjack where a varietyof suspense dynamics can be experimentally induced. Our behavioral dataconfirmed the explanatory power of this theory. We further compared thisformulation with other heuristic models inspired by studies in other do-mains such as narratives and found that most heuristic models cannot wellaccount for the specific temporal dynamics of suspense across wide range ofgame variants. We additionally propose a way to test whether experienc-ing greater levels of suspense motivates more game-playing. In summary,this work is an initial attempt to link formal models of information anduncertainty with affective cognitive states and motivation.
Highlighted Figures
Keywords
Bibtex entry:
@article{li2021expectations,
abstract = {Suspense is a cognitive and affective state that is often experienced in theanticipation of information and contributes to the enjoyment and consump-tion of entertainment such as movies or sports. Ely, Frankel, and Kamenica(2015) proposed a formal definition of suspense which relies upon predictionsabout future belief updates. In order to empirically evaluate this theory, wedesigned a task based on the casino card game Blackjack where a varietyof suspense dynamics can be experimentally induced. Our behavioral dataconfirmed the explanatory power of this theory. We further compared thisformulation with other heuristic models inspired by studies in other do-mains such as narratives and found that most heuristic models cannot wellaccount for the specific temporal dynamics of suspense across wide range ofgame variants. We additionally propose a way to test whether experienc-ing greater levels of suspense motivates more game-playing. In summary,this work is an initial attempt to link formal models of information anduncertainty with affective cognitive states and motivation.},
author = {Li, Z. and Bramley, N.R. and Gureckis, T.M.},
journal = {Cognition and Emotion},
pages = {1--22},
publisher = {Routledge},
title = {Expectations about future learning influence moment-to-moment feelings of suspense},
year = {2021}}QR Code:
Download SVG